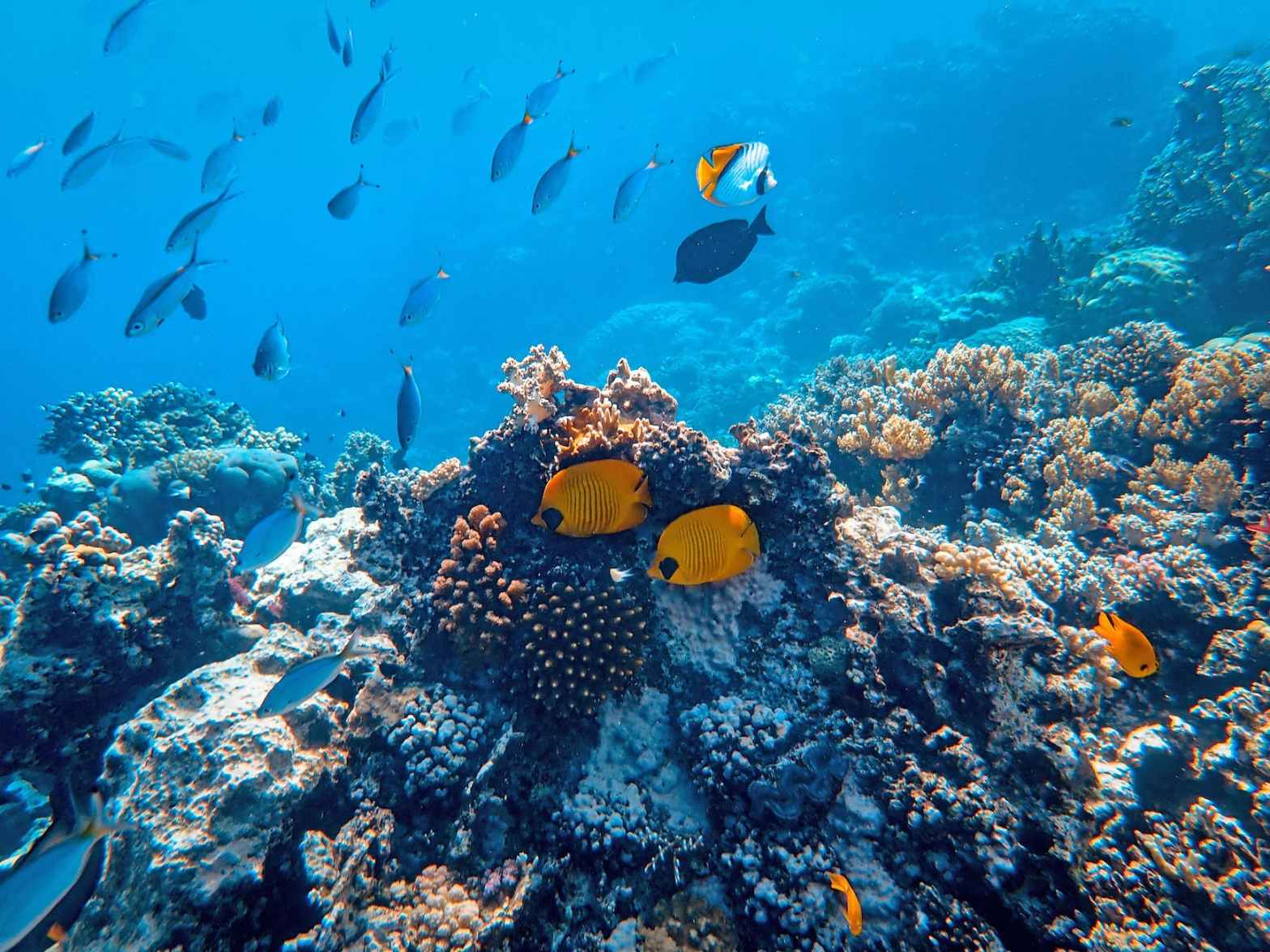
Coral reefs, the vibrant and diverse underwater ecosystems, are under threat due to various human activities. In recent research, it has been revealed that in order to safeguard these fragile ecosystems under the pressures of climate change, mitigating local land and sea-based human impacts is crucial. We want to shed light on the significance of curbing pollutants and over-fishing, particularly along the highly populated shorelines of Hawai’i, to alleviate stress on coral reefs.
Coral reefs around the world are confronted with numerous challenges that compromise their health and resilience. Climate change-induced factors, such as rising ocean temperatures and acidification, have become well-recognized stressors. However, beneath the waves lie additional perils that are equally detrimental, if not more immediate to coral reefs’ survival.
1. Wastewater Pollution: In populated areas along Hawai’i’s shorelines, excessive wastewater pollution emerges as one of the critical culprits affecting coral reef health. Human settlements and coastal infrastructure contribute to the discharge of nutrients and other effluents, elevating the levels of nitrogen and phosphorous in surrounding waters. These pollutants weaken corals, hinder their growth, and render them more susceptible to diseases.
2. Urban Runoff: Another indirect yet harmful consequence of human habitation is the impact of urban runoff on coral reefs. Stormwater carrying sediment, chemicals, and debris flows into the ocean, significantly degrading water quality and negatively modifying the reef’s balance. Excessive sedimentation reduces the amount of sunlight reaching the corals, impeding their photosynthetic capabilities and triggering stress responses.
3. Over-Fishing: Unregulated fishing practices pose a severe threat to coral reef ecosystems. Over-fishing disrupts the delicate ecological balance, removing key species that play vital roles in maintaining reef health. Predatory fish, such as groupers and snappers, control the population of herbivorous fishes, which, in turn, prevents excessive growth of algae that can smother corals. Consequently, unchecked fishing pressure disrupts this natural balance and increases susceptibility to coral decline.
Addressing land and sea-based human impacts is a crucial step in safeguarding coral reefs against the effects of climate change. By reducing local stressors, we enhance the resilience of these ecosystems, enabling them to better withstand the challenges ahead.
1. Improve Wastewater Management: Investing in effective wastewater treatment systems and encouraging proper sewage infrastructure is vital. Implementing advanced treatment methods and enforcing stringent water quality regulations will reduce the excess nutrients introduced into surrounding waters.
2. Promote Sustainable Land Practices: Adopting ecologically sensitive land-use practices can alleviate urban runoff and sedimentation issues. Implementing green infrastructure, such as vegetative buffers and bioretention areas, can filter out pollutants and reduce the volume and velocity of runoff, thus enhancing water quality and protecting coral reefs.
3. Establish Fisheries Management: Enforcing regulations that manage fishing practices, such as size limits, seasonal closures, and protected areas, is crucial in restoring balance to the marine ecosystem. By allowing fish populations to recover and thrive, coral reefs can benefit from the ecological services they provide.
Mitigating local land and sea-based human impacts holds great promise in ensuring the long-term persistence of coral reef ecosystems, especially under the looming threat of climate change.
With the urgency of protecting these fragile underwater wonders, it is imperative that we take decisive action to reduce wastewater pollution, control urban runoff, and establish sustainable fishing practices.
Edited by Zeng Han-Jun
Written by Juliana Rodriguez