According to recent research, the impact of different species and their traits on human wellbeing cannot be overstated. Well-functioning ecosystems are crucial to human health and wellbeing, and human-biodiversity interactions deliver wellbeing gains that can lead to substantial healthcare cost savings when scaled-up across populations.
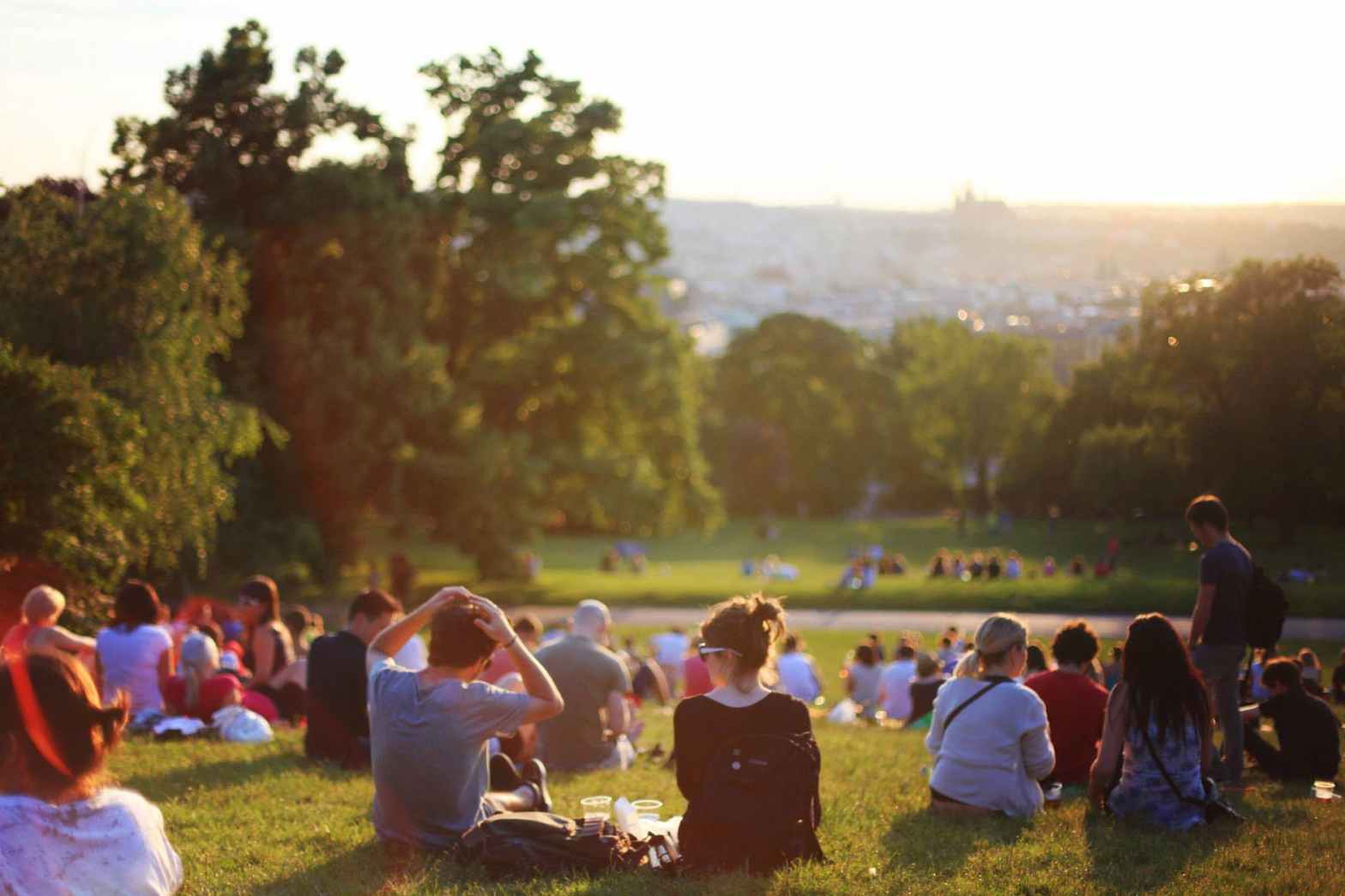
The study showed that the presence of biodiversity in human-inhabited environments leads to increased physical activity and improved mental health.
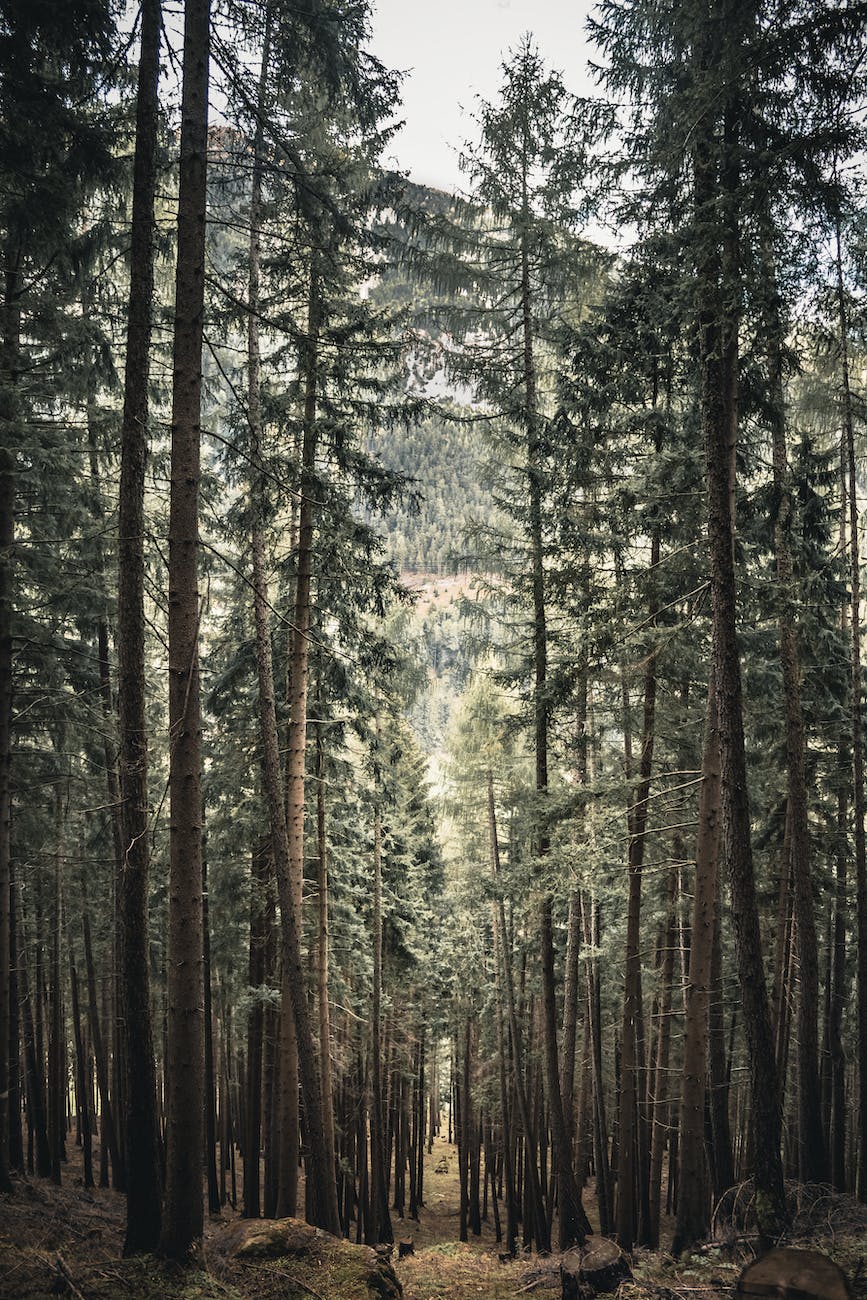
People living in areas with more green space reported feeling less stress and having better overall health than those living in urban areas with less green space.
On top of that, research revealed that contact with nature, such as outdoor activities like hiking or gardening, can improve our immune systems and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic diseases.
Studies have also shown that experiencing nature can reduce blood pressure, lower cortisol levels, and improve overall mood.
Besides this, the research suggests that loss of biodiversity can have critical negative impacts on human wellbeing, as current conditions in many ecosystems are not ideal due to factors such as climate change or habitat loss.
It is essential for human populations to prioritize conservation efforts and enable the restoration of well-functioning ecosystems to ensure long-term human health and wellbeing.
The new research shows that well-functioning ecosystems are crucial to human wellbeing and that human-biodiversity interaction delivers substantial healthcare cost-savings when scaled-up across populations.
Edited by Zeng Han-Jun
Written by Juliana Rodriguez